Introduction
A Cyclopropane Manufacturing Plant Project Report is an essential document for businesses or entrepreneurs seeking to establish a plant to produce cyclopropane, a valuable chemical compound with various industrial applications. Cyclopropane (C3H6) is a colorless, flammable gas primarily used in the pharmaceutical industry, as a refrigerant, and as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals. Given its versatile applications, the demand for cyclopropane is steady across multiple sectors, particularly in medicine, agriculture, and organic chemistry.
This article outlines the process, infrastructure, raw materials, financial considerations, regulatory compliance, and market potential for setting up a cyclopropane manufacturing facility. It is designed to provide you with the necessary insights into this specialized manufacturing business.
What is Cyclopropane?
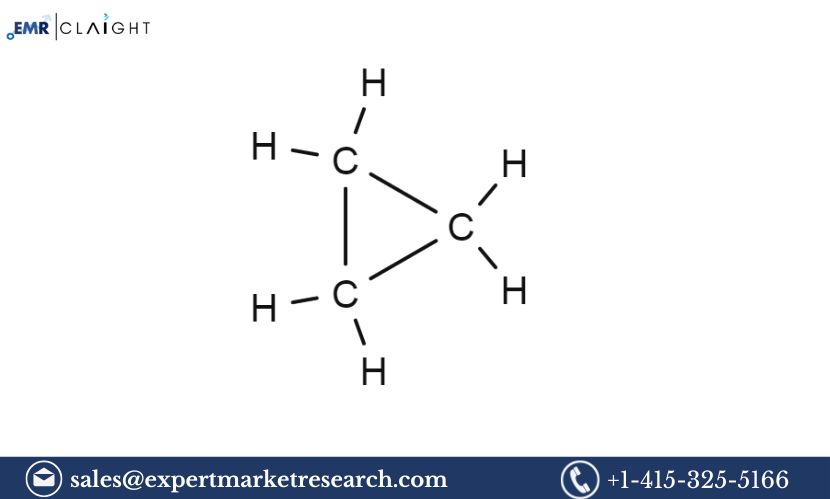
Cyclopropane is a three-membered cyclic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C3H6. It is a colorless, flammable gas with a slightly sweet odor and is highly reactive due to the strain in its three-membered ring structure. Cyclopropane is produced through the hydrogenation of acetylene or by the reaction of ethylene with diazomethane, and it is often used as an anesthetic in the pharmaceutical industry.
It has several important properties:
- Flammability: Cyclopropane is highly flammable and must be handled with care.
- Reactivity: Due to its ring strain, cyclopropane is more reactive than its linear counterparts, which makes it valuable in chemical synthesis.
Cyclopropane is used in the synthesis of other chemicals, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: It has been historically used as an anesthetic (though it has largely been replaced by safer alternatives).
- Chemical Industry: It serves as an intermediate in the production of various chemicals, including certain types of plastics and organic compounds.
- Agriculture: Cyclopropane derivatives are used in the synthesis of plant growth regulators.
- Refrigeration: Cyclopropane was once used as a refrigerant before being largely phased out due to its flammability.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Applications of Cyclopropane
Cyclopropane’s unique chemical properties make it useful in several industries, including:
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Cyclopropane was widely used as an inhalational anesthetic in the mid-20th century, often in combination with other anesthetics. Although safer anesthetics have since replaced cyclopropane in medical applications, it is still used as a precursor for other pharmaceutical compounds.
- Chemical Industry: Cyclopropane is used as a building block in organic chemistry. It participates in various reactions, such as cycloadditions, that help create complex molecules. These reactions are important for producing agrochemicals, plastics, and other industrial chemicals.
- Agriculture: Some derivatives of cyclopropane, like cyclopropene, are used as plant growth regulators, aiding in the regulation of fruit ripening and delaying flowering in certain crops.
- Refrigerants: Historically, cyclopropane was used as a refrigerant. However, due to safety concerns, it has largely been replaced by other refrigerants with lower flammability.
Market Overview of Cyclopropane
The global market for cyclopropane is niche but steady, driven by demand from the pharmaceutical and chemical industries. Despite its limited use compared to other gases and chemicals, cyclopropane’s role as a versatile chemical intermediate ensures that it remains in demand.
Key Market Drivers:
- Pharmaceutical Applications: The pharmaceutical sector’s need for intermediate compounds and the continued demand for cyclopropane derivatives in drug production ensure a constant demand for the gas.
- Chemical Synthesis: Cyclopropane’s utility in creating various organic compounds keeps it relevant in industrial chemical manufacturing.
- Agricultural Demand: The agricultural use of cyclopropane derivatives as growth regulators adds another layer to its market demand.
However, the market faces challenges:
- Safety Concerns: Due to its high flammability, cyclopropane is considered hazardous, which can limit its usage and adoption.
- Competition from Alternatives: Cyclopropane has been replaced in many applications, such as refrigeration, by less hazardous and more cost-effective chemicals.
Production Process of Cyclopropane
Cyclopropane is produced via a number of chemical processes. The most common methods include:
1. Hydrogenation of Acetylene
The most traditional method for producing cyclopropane involves the hydrogenation of acetylene (C2H2) in the presence of a catalyst. This reaction occurs at high temperatures and pressures, where acetylene reacts with hydrogen gas to form cyclopropane.
2. Reaction of Ethylene with Diazomethane
Another method for cyclopropane production involves the reaction of ethylene (C2H4) with diazomethane (CH2N2). This method is typically used on a smaller scale or in laboratory settings.
Raw Materials for Cyclopropane Production
The primary raw materials required for cyclopropane manufacturing include:
- Acetylene (C2H2): Acetylene is one of the primary feedstocks for cyclopropane production through hydrogenation.
- Ethylene (C2H4): Used in the reaction with diazomethane.
- Hydrogen Gas (H2): Used in the hydrogenation of acetylene to cyclopropane.
- Diazomethane (CH2N2): Used in smaller-scale or laboratory production of cyclopropane.
- Catalysts: Depending on the production method, catalysts such as palladium (for hydrogenation) may be required.
Infrastructure and Equipment for Cyclopropane Manufacturing
To set up a cyclopropane manufacturing plant, the following infrastructure and equipment are essential:
- Reaction Vessels: Large reactors are needed for the hydrogenation or diazomethane reaction. These reactors must be capable of handling high pressures and temperatures.
- Hydrogenation Equipment: For the acetylene hydrogenation process, hydrogen compressors, cooling systems, and catalyst chambers are essential.
- Storage Tanks: Cyclopropane is stored in pressurized tanks since it is a gas under normal conditions. Proper storage facilities are needed to maintain safety standards.
- Purification Units: Cyclopropane produced through hydrogenation or other methods may contain impurities. A purification unit is necessary to ensure the product meets quality specifications.
- Safety Systems: Given the flammability of cyclopropane, safety equipment such as explosion-proof systems, leak detectors, and fire suppression systems are essential.
- Packaging and Distribution: Cyclopropane is generally distributed in compressed gas cylinders or larger storage containers, so packaging and distribution systems are necessary.
Financial Considerations and Investment
Setting up a cyclopropane manufacturing plant involves significant financial investment. Key considerations include:
- Capital Investment: Costs for plant construction, machinery, and storage tanks can be substantial. Specialized equipment for hydrogenation, purification, and storage will also require a significant initial outlay.
- Raw Material Costs: The cost of acetylene, ethylene, and other chemicals used in production will vary based on market conditions.
- Operating Costs: Labor, maintenance, energy consumption, and other day-to-day expenses must be factored in.
- Regulatory Costs: Compliance with health, safety, and environmental regulations can incur additional costs, including certification, waste management, and environmental audits.
- Market and Distribution Costs: Establishing distribution networks and marketing the product will also require capital.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Cyclopropane is a flammable gas, and its production and distribution are subject to various safety and environmental regulations. Some key compliance requirements include:
- Safety Standards: Cyclopropane production facilities must adhere to stringent safety regulations to mitigate the risks associated with flammability and toxicity.
- Environmental Regulations: The plant must comply with regulations on air emissions, waste disposal, and chemical handling to minimize environmental impact.
- Health and Safety: Proper training for employees and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential to ensure workplace safety.
- Transportation Regulations: The transportation of cyclopropane in cylinders or larger containers must comply with local and international regulations for hazardous materials.
Market Research and Feasibility Study
Before embarking on the establishment of a cyclopropane manufacturing plant, a detailed market research and feasibility study should be conducted. This study should assess:
- Market Demand: Understanding demand from the pharmaceutical, chemical, and agricultural sectors for cyclopropane and its derivatives.
- Competitive Analysis: Identifying key competitors in the cyclopropane market and analyzing their production capacity, pricing, and market share.
- Profitability: Estimating production costs, revenue, and ROI based on market conditions and sales forecasts.
FAQ
1. What is cyclopropane used for?
Cyclopropane is used primarily as a chemical intermediate, in pharmaceuticals (especially as a historical anesthetic), and in the production of plant growth regulators and organic compounds.
2. How is cyclopropane produced?
Cyclopropane is produced mainly through the hydrogenation of acetylene or the reaction of ethylene with diazomethane.
3. What are the raw materials required for cyclopropane production?
The main raw materials are acetylene, ethylene, hydrogen gas, and diazomethane.
4. Is cyclopropane hazardous?
Yes, cyclopropane is highly flammable and reactive, which requires careful handling during its production and storage.
5. What industries use cyclopropane?
Cyclopropane is used in the pharmaceutical industry, chemical manufacturing, and agriculture, particularly for plant growth regulation.
6. What are the safety concerns in cyclopropane production?
Due to its flammability, cyclopropane production facilities must implement strict safety measures to prevent fires or explosions.
Related Reports
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au/reports/australia-feed-additives-market
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au/reports/australia-hair-oil-market
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au/reports/australia-home-shopping-market
Media Contact:
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au